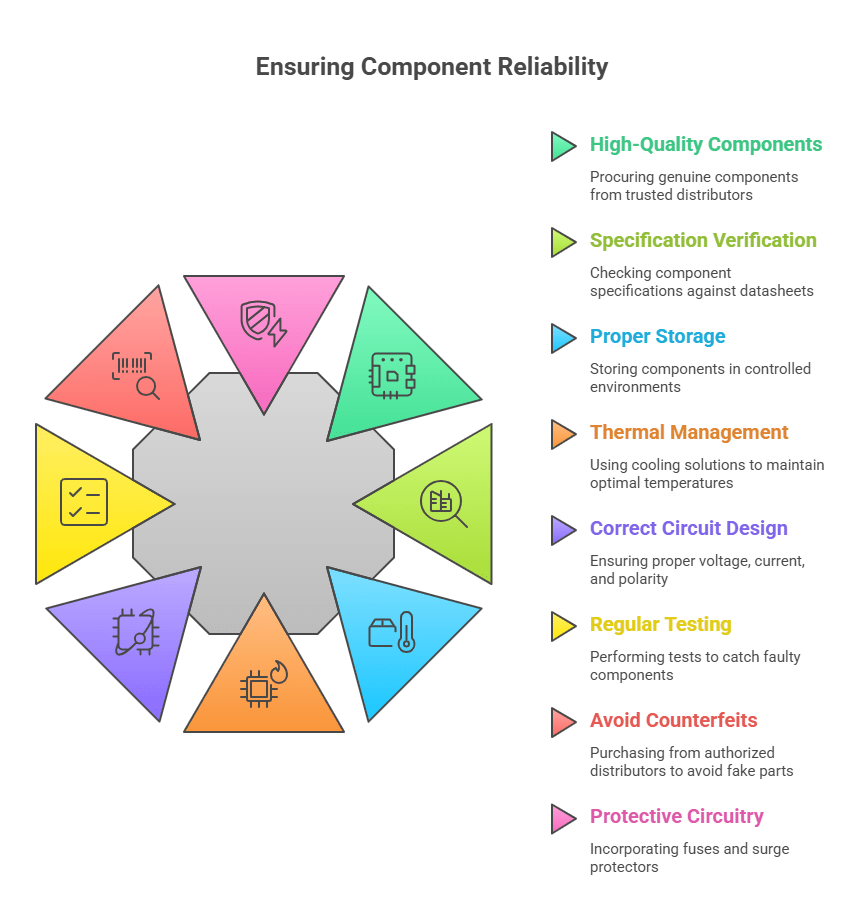
Everything You Need to Know About Switches in Electronics
Switches are one of the most important parts of electronics. From simple household items like lights and fans to big machines in factories, switches help us control electricity easily and safely. Every time you press a button, flip a switch, or turn a knob, you are using a switch to control how electricity flows. In this blog, we’ll understand what switches are, how they work, the different types of switches, and where they are used — all in simple words.